Taysha IPO Presentation Deck
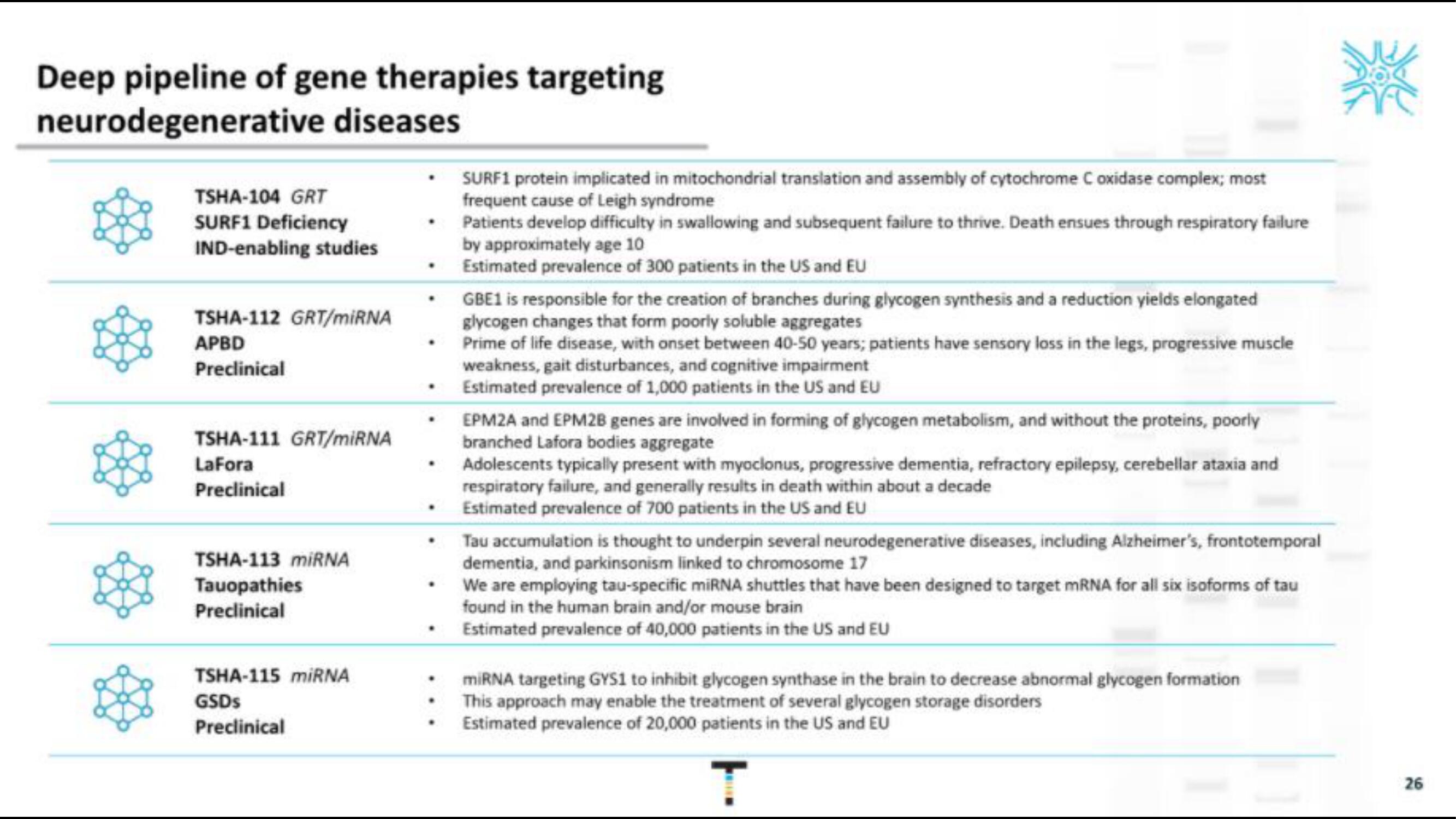
Deep pipeline of gene therapies targeting
neurodegenerative diseases
TSHA-104 GRT
SURF1 Deficiency
IND-enabling studies
TSHA-112 GRT/miRNA
APBD
Preclinical
TSHA-111 GRT/miRNA
LaFora
Preclinical
TSHA-113 miRNA
Tauopathies
Preclinical
TSHA-115 miRNA
GSDs
Preclinical
SURF1 protein implicated in mitochondrial translation and assembly of cytochrome C oxidase complex; most
frequent cause of Leigh syndrome
Patients develop difficulty in swallowing and subsequent failure to thrive. Death ensues through respiratory failure
by approximately age 10
Estimated prevalence of 300 patients in the US and EU
GBE1 is responsible for the creation of branches during glycogen synthesis and a reduction yields elongated
glycogen changes that form poorly soluble aggregates
Prime of life disease, with onset between 40-50 years; patients have sensory loss in the legs, progressive muscle
weakness, gait disturbances, and cognitive impairment
Estimated prevalence of 1,000 patients in the US and EU
• EPM2A and EPM2B genes are involved in forming of glycogen metabolism, and without the proteins, poorly
branched Lafora bodies aggregate
Adolescents typically present with myoclonus, progressive dementia, refractory epilepsy, cerebellar ataxia and
respiratory failure, and generally results in death within about a decade
Estimated prevalence of 700 patients in the US and EU
Tau accumulation is thought to underpin several neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's, frontotemporal
dementia, and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17
We are employing tau-specific miRNA shuttles that have been designed to target mRNA for all six isoforms of tau
found in the human brain and/or mouse brain
Estimated prevalence of 40,000 patients in the US and EU
miRNA targeting GYS1 to inhibit glycogen synthase in the brain to decrease abnormal glycogen formation
This approach may enable the treatment of several glycogen storage disorders
Estimated prevalence of 20,000 patients in the US and EU
*
26View entire presentation