Taysha IPO Presentation Deck
Mutations in KCNQ2 result in severe
neonatal epilepsy syndromes
-
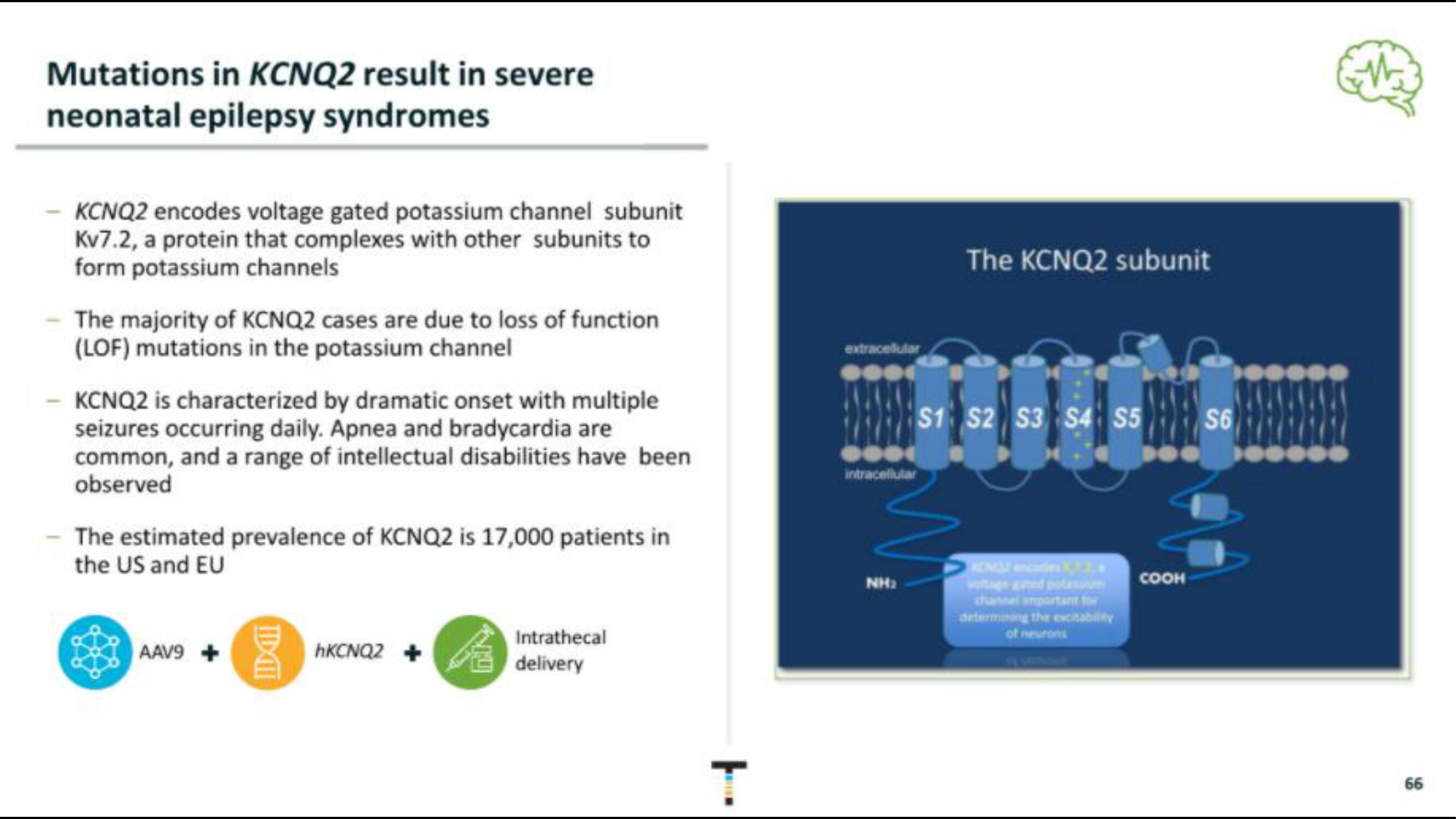
KCNQ2 encodes voltage gated potassium channel subunit
Kv7.2, a protein that complexes with other subunits to
form potassium channels
The majority of KCNQ2 cases are due to loss of function
(LOF) mutations in the potassium channel
KCNQ2 is characterized by dramatic onset with multiple
seizures occurring daily. Apnea and bradycardia are
common, and a range of intellectual disabilities have been
observed
The estimated prevalence of KCNQ2 is 17,000 patients in
the US and EU
AAV9+
IXT
hKCNQZ
Intrathecal
delivery
extracellular
intracellular
NH₂
The KCNQ2 subunit
S1 S2 S3 S4 S5
KONC37 encades (IZA
channel important for
determining the excitability
of neurons
COOH
S6
66View entire presentation