Optimizing Design and Controls for Thermal Energy Storage
Finite Difference Model
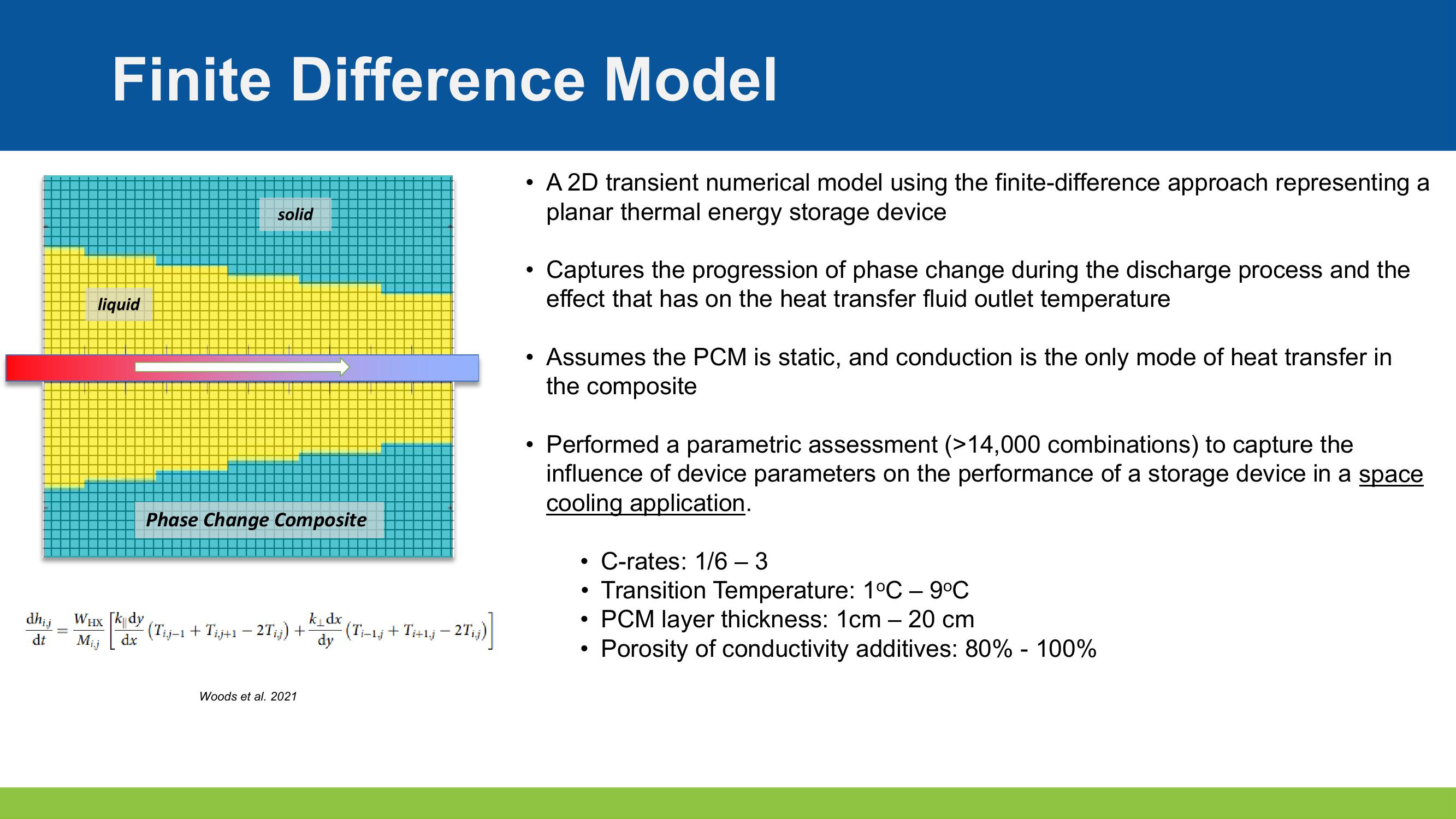
liquid
solid
Phase Change Composite
•
•
A 2D transient numerical model using the finite-difference approach representing a
planar thermal energy storage device.
Captures the progression of phase change during the discharge process and the
effect that has on the heat transfer fluid outlet temperature
Assumes the PCM is static, and conduction is the only mode of heat transfer in
the composite
• Performed a parametric assessment (>14,000 combinations) to capture the
influence of device parameters on the performance of a storage device in a space
cooling application.
•
C-rates: 1/6 - 3
Transition Temperature: 1°C -9°C
PCM layer thickness: 1cm - 20 cm
·
dhij
WHX [k dy
kdx
dt
Mi.j
dx
(Tij-1+ Tij+1-2Ti,j) +
(Ti−1,j + Ti+1j − 2Tij)
-
dy
•
Porosity of conductivity additives: 80% - 100%
Woods et al. 2021View entire presentation