Taysha IPO Presentation Deck
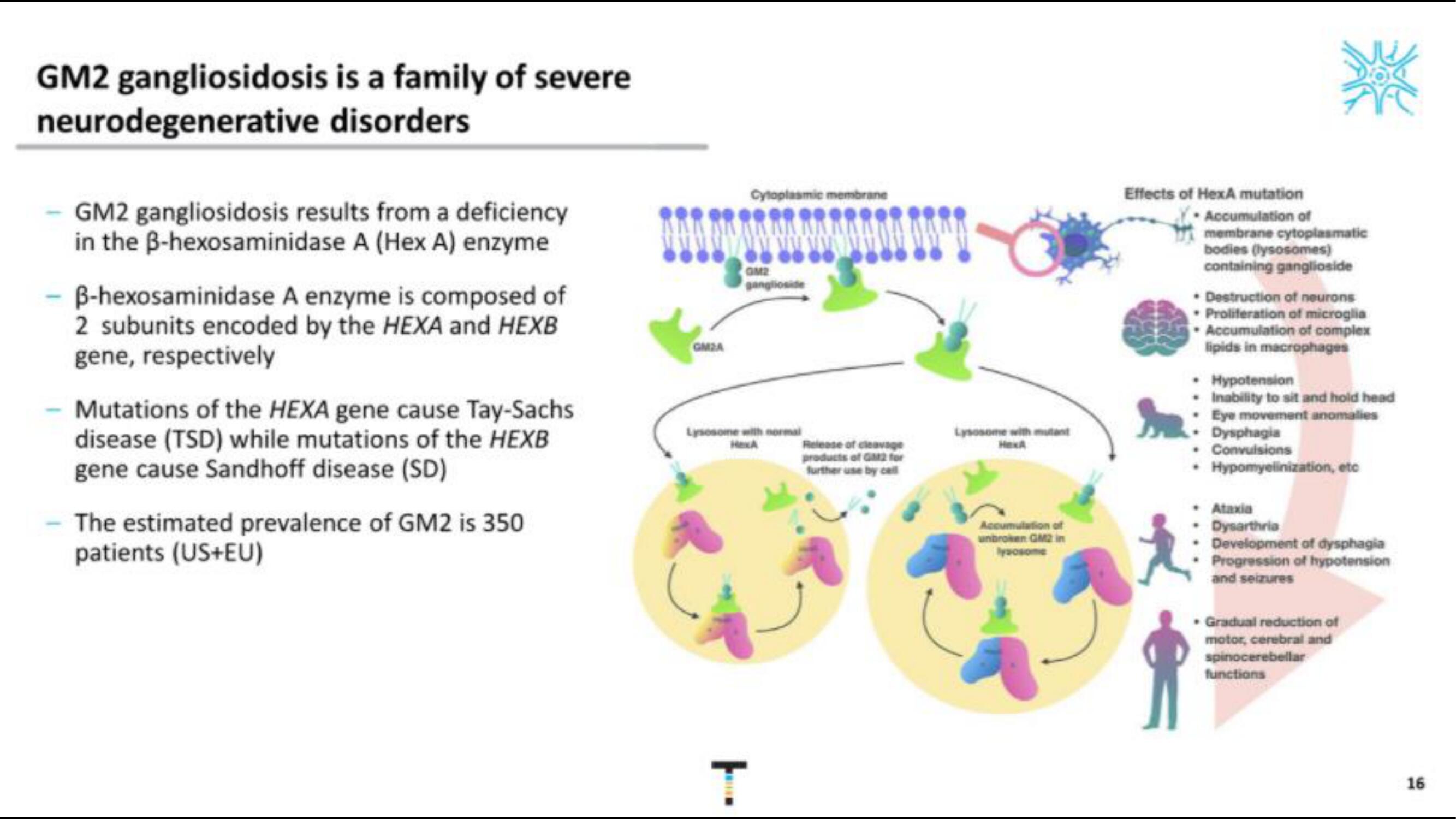
GM2 gangliosidosis is a family of severe
neurodegenerative
disorders
GM2 gangliosidosis results from a deficiency
in the B-hexosaminidase A (Hex A) enzyme
B-hexosaminidase A enzyme is composed of
2 subunits encoded by the HEXA and HEXB
gene, respectively
Mutations of the HEXA gene cause Tay-Sachs
disease (TSD) while mutations of the HEXB
gene cause Sandhoff disease (SD)
- The estimated prevalence of GM2 is 350
patients (US+EU)
GMZA
Cytoplasmic membrane
GM2
ganglioside
Lysosome with normal
HexA
F.
Release of cleavage
products of GM2 for
further use by cell
DOPO
Lysosome with mutant
HexA
Accumulation of
unbroken GM2 in
lysosome
Effects of HexA mutation
Accumulation of
membrane cytoplasmatic
bodies (lysosomes)
containing ganglioside
A
*
• Destruction of neurons
Proliferation of microglia
Accumulation of complex
lipids in macrophages
. Hypotension
. Inability to sit and hold head
Eye movement anomalies
Dysphagia
. Convulsions
Hypomyelinization, etc
. Ataxia
. Dysarthria
Development of dysphagia
Progression of hypotension
and seizures
. Gradual reduction of
motor, cerebral and
spinocerebellar
functions
16View entire presentation