ATAI Investor Presentation Deck
SUMMARY
There is an unmet need
in GAD for therapies
with rapid onset, high
efficacy, and minimal
side effects
SSRI's are current standard of care
for GAD but require 4-6 weeks for
onset of effect and have several
disadvantages¹:
1. SSRI/SNRI-specific inadequacy
2. Lack of tolerability
3. Patient nonadherence to
medications that fail to
relieve symptoms of anxiety
quickly
Benzodiazepines are second-line
treatment, offering fast and
effective relief, but carrying
significant risk of:
1. Sedation
2. Impaired cognition
3. Dependence/addiction
I
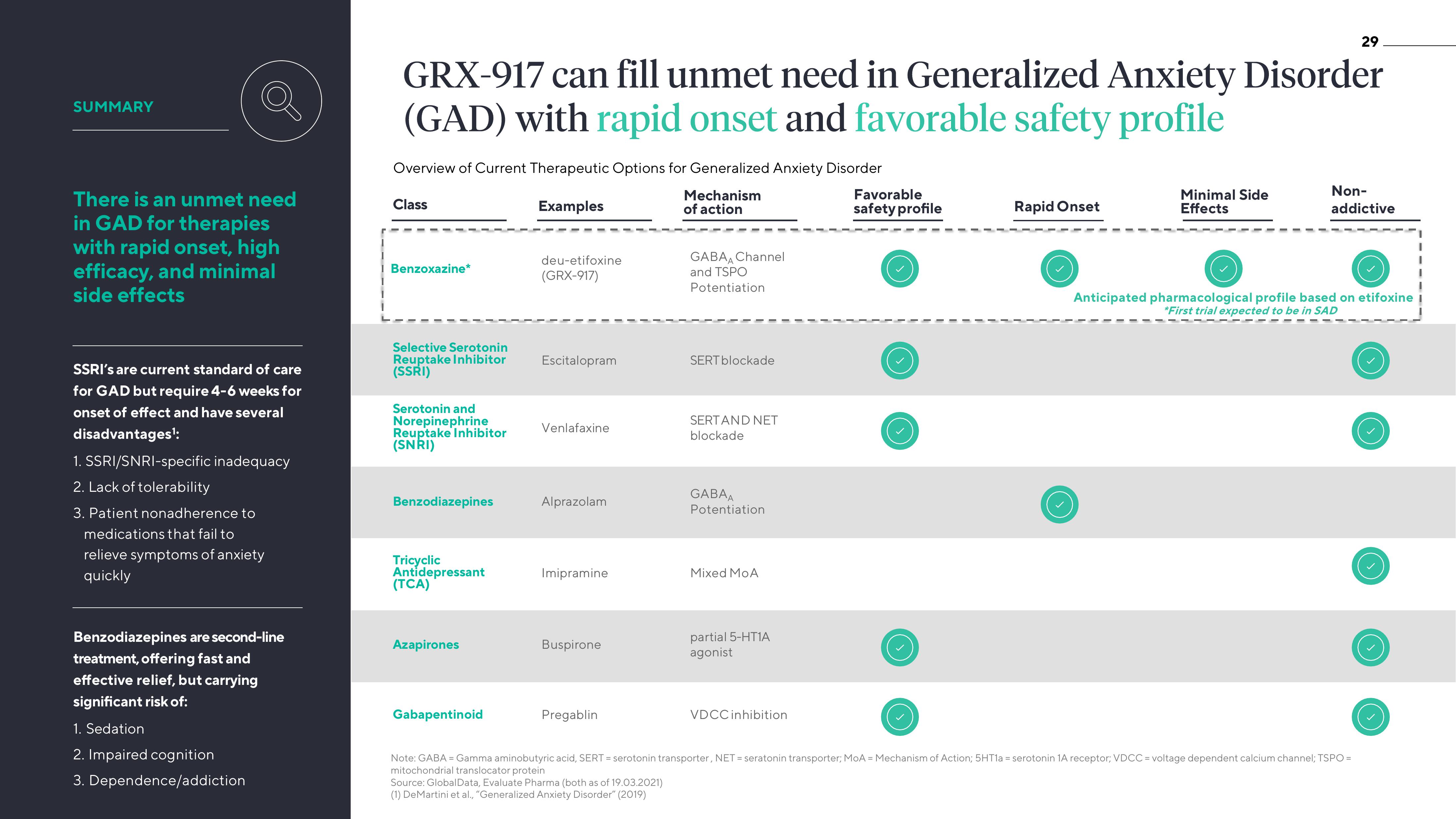
GRX-917 can fill unmet need in Generalized Anxiety Disorder
(GAD) with rapid onset and favorable safety profile
Overview of Current Therapeutic Options for Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Examples
Mechanism
of action
Class
Benzoxazine*
Selective Serotonin
Reuptake Inhibitor
(SSRI)
Serotonin and
Norepinephrine
Reuptake Inhibitor
(SNRI)
Benzodiazepines
Tricyclic
Antidepressant
(TCA)
Azapirones
Gabapentinoid
deu-etifoxine
(GRX-917)
Escitalopram
Venlafaxine
Alprazolam
Imipramine
Buspirone
Pregablin
GABA Channel
and TSPO
Potentiation
Source: Global Data, Evaluate Pharma (both as of 19.03.2021)
(1) DeMartini et al., "Generalized Anxiety Disorder" (2019)
SERT blockade
SERTAND NET
blockade
GABAA
Potentiation
Mixed MoA
partial 5-HT1A
agonist
VDCC inhibition
Favorable
safety profile
Rapid Onset
Minimal Side
Effects
29
Non-
addictive
Note: GABA = Gamma aminobutyric acid, SERT = serotonin transporter, NET = seratonin transporter; MoA = Mechanism of Action; 5HT1a = serotonin 1A receptor; VDCC = voltage dependent calcium channel; TSPO=
mitochondrial translocator protein
Anticipated pharmacological profile based on etifoxine
*First trial expected to be in SADView entire presentation