Spring 2023 Solar Industry Update
Generation (TWh)
Capacity (GW)
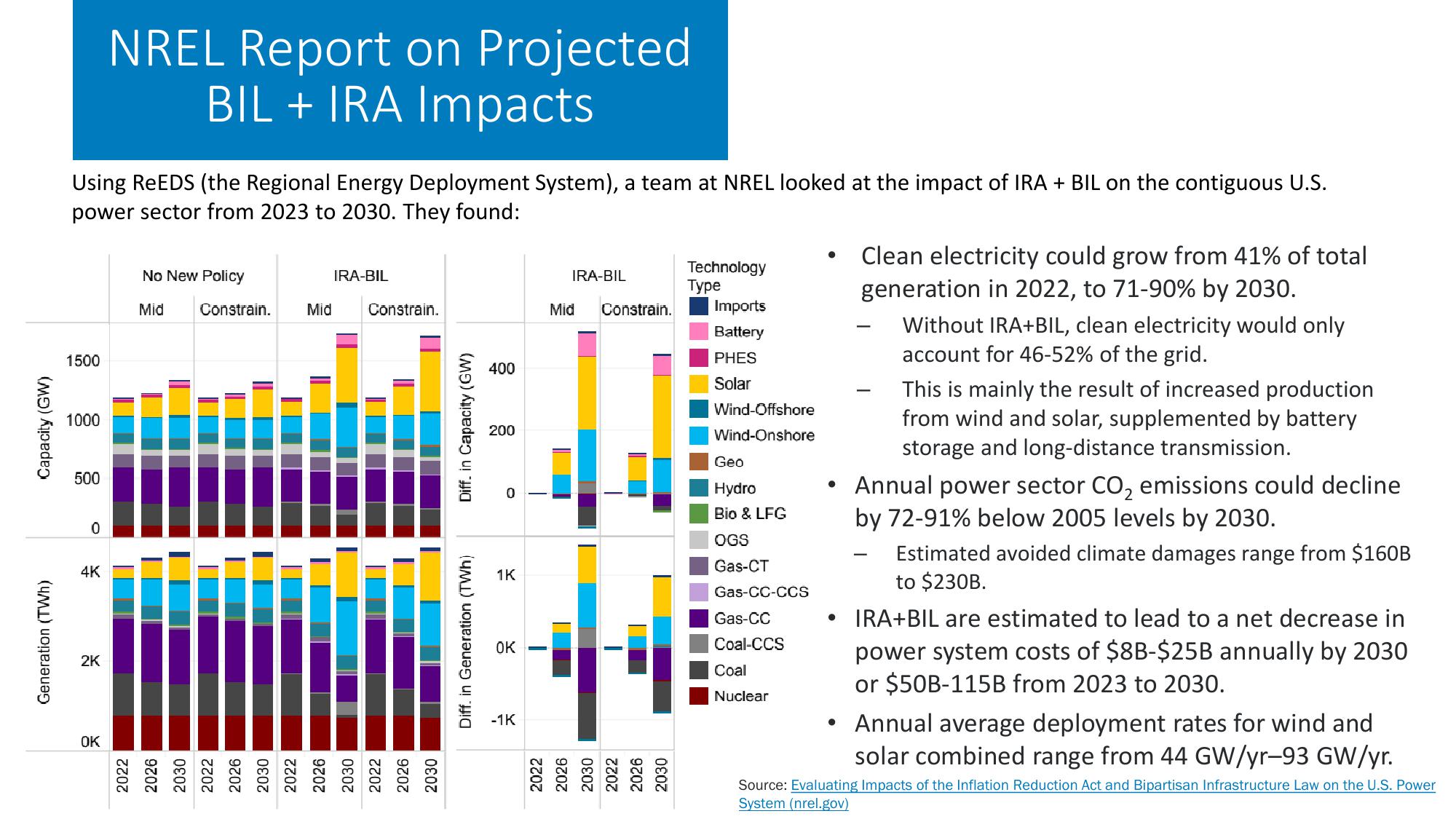
NREL Report on Projected
BIL + IRA Impacts
Using ReEDS (the Regional Energy Deployment System), a team at NREL looked at the impact of IRA + BIL on the contiguous U.S.
power sector from 2023 to 2030. They found:
1500
1000
500
0
44
4K
2K
OK
No New Policy
Mid
IRA-BIL
Constrain.
Mid
Constrain.
2022
2026
2030
2022
2026
2030
2022
2026
2030
Diff. in Generation (TWh)
Diff. in Capacity (GW)
400
200
0
1K
HI
OK
-1K
IRA-BIL
Technology
Type
Mid
Constrain.
Imports
Battery
PHES
2022
2026
2030
2022
2026
2030
Solar
Wind-Offshore
Wind-Onshore
Geo
Hydro
Bio & LFG
OGS
Gas-CT
Gas-CC-CCS
Gas-CC
Coal-CCS
Coal
Nuclear
.
Clean electricity could grow from 41% of total
generation in 2022, to 71-90% by 2030.
Without IRA+BIL, clean electricity would only
account for 46-52% of the grid.
This is mainly the result of increased production
from wind and solar, supplemented by battery
storage and long-distance transmission.
Annual power sector CO2 emissions could decline
by 72-91% below 2005 levels by 2030.
Estimated avoided climate damages range from $160B
to $230B.
IRA+BIL are estimated to lead to a net decrease in
power system costs of $8B-$25B annually by 2030
or $50B-115B from 2023 to 2030.
Annual average deployment rates for wind and
solar combined range from 44 GW/yr-93 GW/yr.
Source: Evaluating Impacts of the Inflation Reduction Act and Bipartisan Infrastructure Law on the U.S. Power
System (nrel.gov)View entire presentation